The Standard Template Adaptive Parallel Library (STAPL) comprises several sections: Run-time System, Paragraph, Skeletons Framework, pContainers,
pViews, and pAlgorithms.
STAPL's run-time system (RTS) provides to the Developer and Specialist
the following facilities:
Communication primitives, based on Adaptive Remote Method
Invocation (ARMI);
Executor of pRange's tasks that enforces tasks dependencies;
User definable scheduler for the tasks of pRanges;
Performance Monitor for adaptiveness and for user feedback.
ARMI communication library hides all the details about the underlying
platform, by being implemented over the lower level communication facilities,
such as MPI, OpenMP, Pthreads, etc. The communication interface
supports a well defined consistency model to allow the developers to
design algorithms in a uniform and portable way.
PARAGRAPH is the STAPL data flow engine which allows parallelism to be expressed explicitly using data flow graphs (a.k.a. task graphs).
The STAPL Skeleton Framework is an interface for algorithm development which helps developers to only focus on defining their computation
in terms of skeletons. Each skeleton is translated to a parametric data flow graph and is expanded upon the presence of input data. The
data flow representation of skeletons allows programs to run on distributed and shared memory systems.
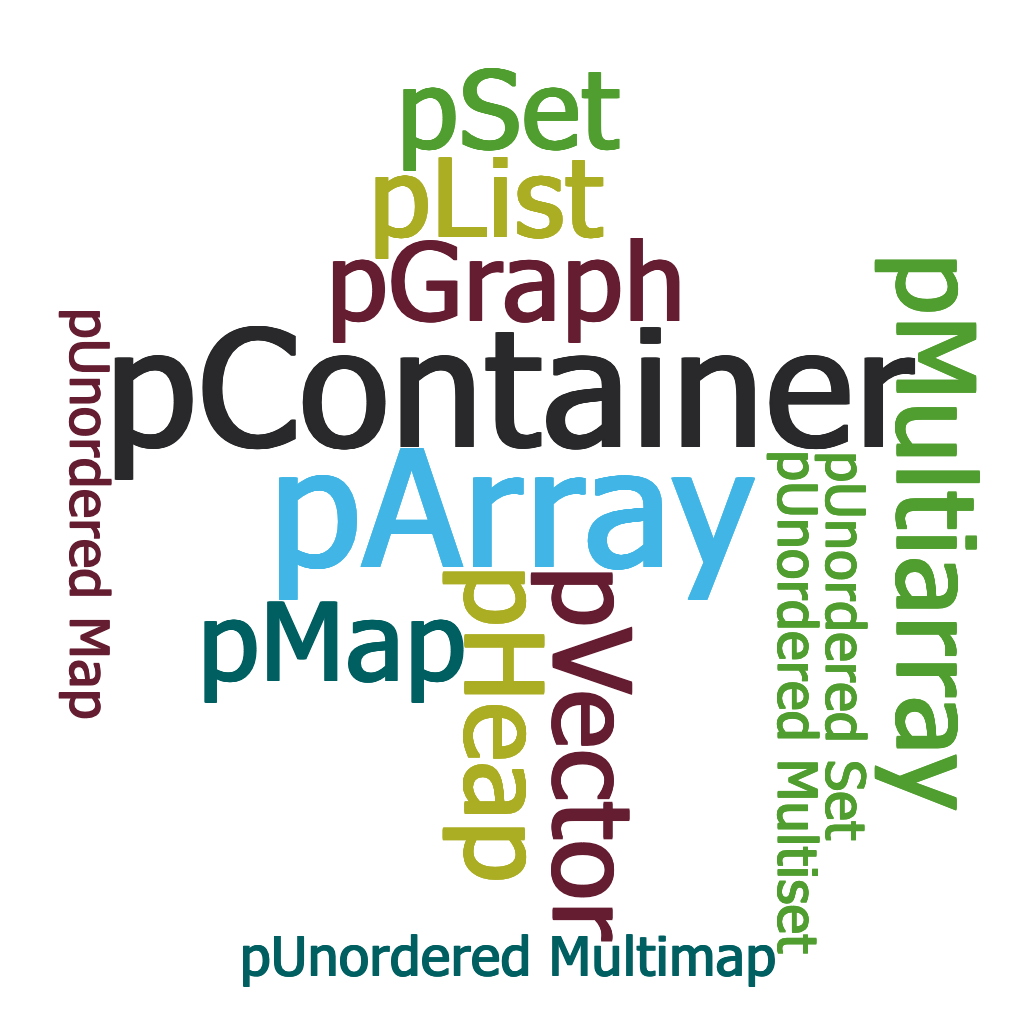
A pContainer is a distributed data structures that have interfaces similar to the (sequential) C++ standard library (stl). Its data is
partitioned and distributed across the machine, but the User is offered a shared object view. The pContainer distribution across the machine can be user
specified or automatically selected by STAPL. STAPL provides a large number of basic data parallel structures (e.g., pArray, pList, pVector, pGraph,
pMap, pSet).
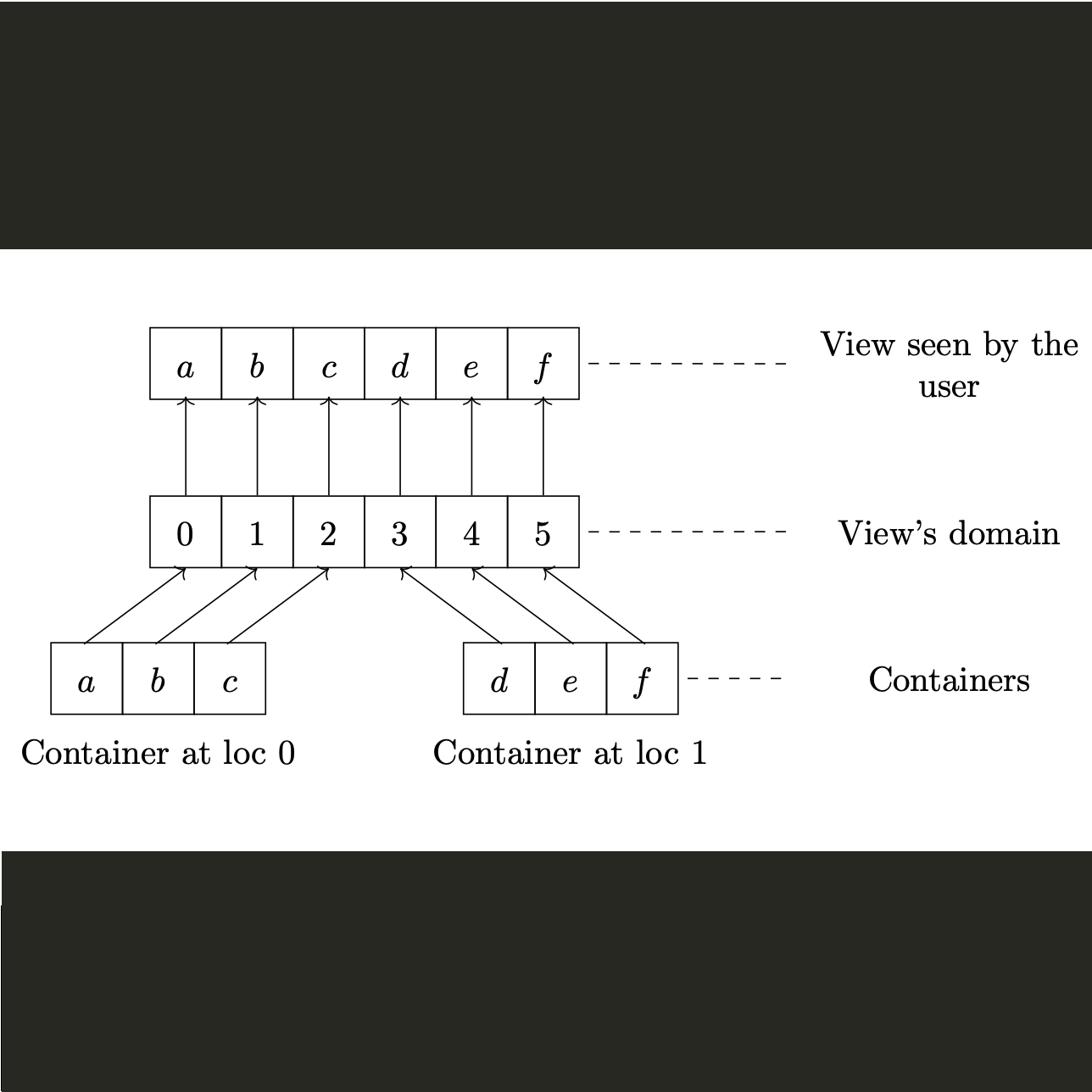
pViews are the STAPL equivalent of STL iterators in the sense
that they provide a generic mechanism to access the data of the
pContainers. pViews emphasize processing data ranges over accessing
single items. Each pView may be partitioned into subviews
hierarchically and this allow to adjust the degree of parallelism to
the application needs and nested parallelsm.
A pAlgorithm is the parallel equivalent of an STL
algorithm. A pAlgorithm is written in terms of pViews operations. The
hierarchical structure of input pViews and the algorithm access pattern
decide the degree of parallelism available for computation. A
pAlgorithm can modify input pViews for optimized data access and/or
easier algorithm specification.
The STAPL Graph Library (SGL)
is a distributed-memory high-performance parallel graph processing framework written in C++ using STAPL.
In addition to a graph data structure, SGL includes a collection of efficient parallel graph algorithms.